Researchers Use AI to Predict Cancer Risk of Lung Nodules
Model appears to work equally well on diagnostic and low-dose screening CT

An AI tool helps doctors predict the cancer risk in lung nodules seen on CT, according to a new study published in Radiology.
Pulmonary nodules appear as small spots on the lungs on chest imaging. They have become a much more common finding as CT has gained favor over X-rays for chest imaging.
“A nodule would appear on somewhere between 5% to 8% of chest X-rays,” said study senior author Anil Vachani, MD, director of clinical research in the section of Interventional Pulmonology and Thoracic Oncology at the Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia. “Chest CT is such a sensitive test, you’ll see a small nodule in upwards of a third to a half of cases. We’ve gone from a problem that was relatively uncommon to one that affects 1.6 million people in the U.S. every year.”
Dr. Vachani and colleagues evaluated an AI-based computer-aided diagnosis tool developed by Optellum Ltd. of Oxford, England, to assist clinicians in assessing pulmonary nodules on chest CT. While CT scans show many aspects of the nodule, such as size and border characteristics, AI can delve even deeper.
“AI can go through very large datasets to come up with unique patterns that can’t be seen through the naked eye and end up being predictive of malignancy,” Dr. Vachani said.
Decision Making Is Better but More Study Is Needed
In the study, six radiologists and six pulmonologists made estimates of malignancy risk for nodules using CT imaging data alone. They also made management recommendations such as CT surveillance or a diagnostic procedure for each case without and with the AI tool.
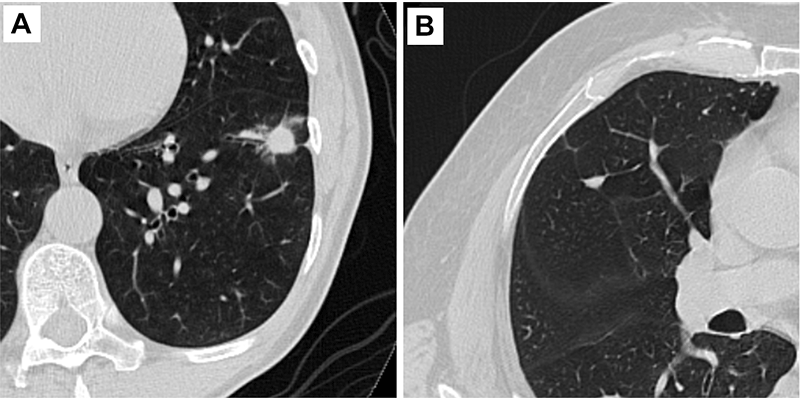
Representative axial CT images of pulmonary nodules included in the study. (A) Malignant nodule with a lung cancer prediction score of 10. (B) Benign nodule with a lung cancer prediction score of 2.
Kim et al, Radiology 2022; 000:1-9 © RSNA 2022
A total of 300 chest CTs of indeterminant pulmonary nodules were used in the study. The researchers defined indeterminant nodules as those between 5 and 30 millimeters in diameter.
Analysis showed that use of the AI tool improved estimation of nodule malignancy risk on chest CT. It also improved agreement among the different readers for both risk stratification and management recommendations.
“The readers judge malignant or benign with a reasonable level of accuracy based on imaging itself, but when you combine their clinical interpretation with the AI algorithm, the accuracy level improves significantly,” Dr. Vachani said. “The level of improvement suggests that this tool has the potential to change how we judge cancer versus benign and hopefully improve how we manage patients.”
The model appears to work equally well on diagnostic CT and low-dose screening CT, Dr. Vachani said, but more study is needed before the AI tool can be used in the clinic.
“We’ve taken the first step here and shown that decision making is better if the AI tool is incorporated into radiology or pulmonology practice,” Dr. Vachani said. “The next step is to take the tool and do some prospective trials where physicians use the AI tool in a real-world setting. We are in the process of designing those trials.”
For More Information
Access the Radiology study, “Artificial Intelligence Tool for Assessment of Indeterminate Pulmonary Nodules Detected with CT.”
Access the related Radiology editorial, “Artificial Intelligence Improves Radiologist Performance for Predicting Malignancy at Chest CT.”
Read previous RSNA News stories about lung cancer imaging: