Ultrasound Effective at Diagnosing Localized Breast Lumps, Pain
Approach may be especially beneficial in low- or middle-income countries

Ultrasound is an effective standalone diagnostic method in patients with focal breast complaints, according to a study published in Radiology. Focal breast complaints can refer to pain, lumps, nipple discharge or other symptoms and conditions.
In the Netherlands, approximately 70,000 women—many between the ages of 30 and 50 years—visit radiology departments annually with focal breast complaints with the most common being the presence of lumps or pain.
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) followed by targeted US is the standard diagnostic tool for women 30 years or older with localized breast complaints. While DBT provides an overall image of both breasts, US can achieve more targeted imaging of a specific area of the breast.
For the new study, researchers set out to investigate the performance of US alone as an effective diagnostic method in women over the age of 30 who reported localized breast complaints at three hospitals in the Netherlands between September 2017 and June 2019.
“The evaluation of breast complaints is a common problem in breast diagnostics,” said study co-author Linda Appelman, MD, a breast radiologist in the Department of Medical Imaging at Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, the Netherlands. “Ultrasound as the first imaging method may provide clarity with regard to the focal breast complaint.”
Breast lumps or localized breast pain were two of the most common symptoms reported by the 1,961 women included in the study. A total of seven subgroups of focal complaints were recognized.
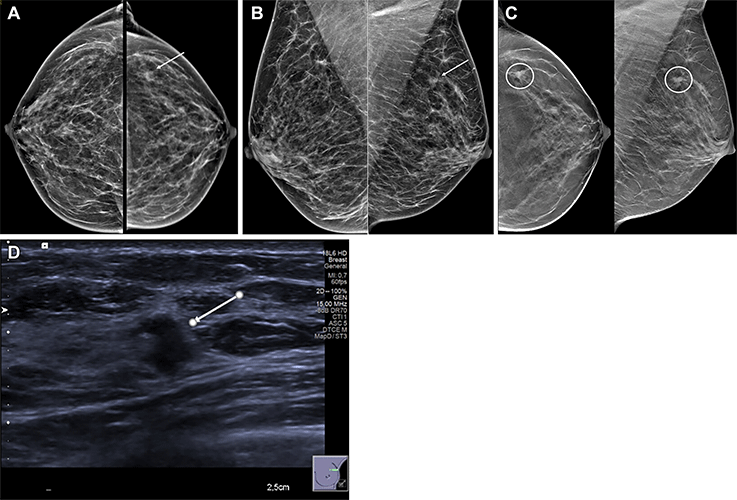
Images in a 54-year-old woman show a palpable lump in the right breast and an irregular mass in the left breast. Mammographic evaluation of the right breast was normal. (A, B) Craniocaudal (A) and mediolateral oblique (B) views of synthesized mammograms and (C) tomosynthesis image in craniocaudal and mediolateral oblique view of the left breast show an architectural distortion with mass (arrow in A and B, circles in C). (D) Targeted US scan at the site of the incidental finding shows an 8-mm hypoechogenic irregular solid mass with indistinct margins (arrow). US-guided biopsy showed invasive ductal carcinoma, grade I.
https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiol.220361 © RSNA 2023
Cost Effectiveness and Improved Patient Comfort Among Factors to Consider
In all patients, targeted US was evaluated first, followed by DBT. Biopsy was performed after US, if needed. Analysis showed that US alone led to accurate diagnosis in 1,759 (90%) of the 1,961 patients. Over 80% of the complaints ended up being normal or benign findings.
“We found that the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasound is high in women with focal breast complaints,” Dr. Appelman said.
A total of 374 patients had biopsies based on US findings alone. This resulted in 192 symptomatic breast cancer diagnoses.
The use of US to evaluate focal breast complaints may be especially beneficial in low- or middle-income countries where US is more readily available than DBT.
“Our study showed that ultrasound alone can effectively diagnose focal breast complaints in a large majority of women,” Dr. Appelman said. “In a setting with limited resources or an already existing screening program, initial ultrasound might be a better alternative compared to mammography.”
The cost effectiveness of US and the improved patient comfort during the procedure are other factors to consider when expanding its implementation in symptomatic breast cancer diagnosis.
For More Information
Access the Radiology study, “US and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Women with Focal Breast Complaints: Results of the Breast US Trial (BUST) and the related editorial.
Read previous RSNA News stories about breast imaging: