Researchers Advance MR Neurography
Researchers report on the impact of cutting-edge MR neurography techniques in chronic pain


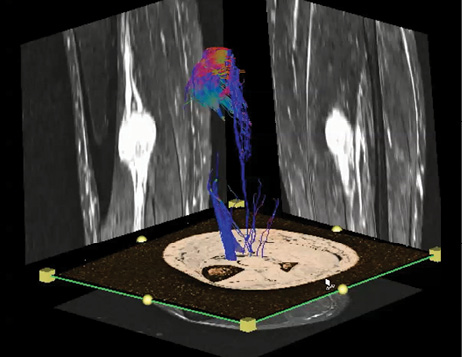
MR Neurography of the Lumbar Plexus and Lower Extremities
Lumbosacral plexus has a complex anatomy with numerous nerve convergences and divergences resulting in the formation of multiple essential peripheral nerves that provide motor and sensory function to the pelvis and lower extremities. Due to the deep location and complexity, 3-D MR neurography (MRN) plays a major role in the evaluation of its normal and pathologic states.
At RSNA 2014, Avneesh Chhabra, M.D., chief musculoskeletal radiologist and associate professor of diagnostic radiology and orthopedic surgery at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, discussed the role MRN plays in chronic pelvic pain, nerve injuries, entrapments and diffuse neuropathies. Along with discussing the incremental value of MRN over conventional lumbar spine imaging, Dr. Chhabra addressed new 3-D techniques that encompass diffusion and motion-sensitive driven equilibrium pulses and suppress vascular signals effectively while preserving selective nerve visualization in neurovascular bundles.
“It is essential to objectively visualize and evaluate nerve anatomy and pathology with multiplanar MRN techniques rather than just identifying indirect findings of neuropathy on lumbar spine imaging or regional muscle imaging,” said Dr. Chhabra, also an adjunct professor at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore. “MRN results significantly impact patient management and outcomes.”
Video
Access research on this topic co-authored by Dr. Chhabra at NCBI.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed. A video of Dr. Chhabra discussing high-resolution MRN and MR-guided injections is available at Hopkinsradiology.org/Musculoskeletal/Neurography.
DTI of the Peripheral Nervous System
While diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is an established imaging technique in the brain and central nervous system, its application to the peripheral nervous system has been limited due to technical reasons.
But recent research has not only shown that the technique can be applied successfully to imaging peripheral nerves, but that it exhibits a high sensitivity and specificity for detecting peripheral nerve injuries and other neuropathies, according to RSNA 2014 presenter Gustav Andreisek, M.D., senior radiologist at the University Hospital Zurich. DTI may also serve as a biomarker for the demyelination of axons and the extent of nerve fiber loss, he said.
“With diffusion tensor imaging of peripheral nerves, we cross the border of pure morphological imaging and move on to functional imaging. This will generate information of much higher value to the referring clinician, enabling an earlier and more precise treatment of patients with peripheral neuropathies. The sites where DTI is already used in the clinical routine report improvements in patient management and likely outcome," Dr. Andreisek said.
Research on this issue co-authored by Dr. Andreisek is available at Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=andreisek.