Steroid Injections of Hip and Knee May Damage Joints
Researchers recommend adding injection-associated risks to patient consent forms

Corticosteroid injections used to treat osteoarthritis pain in the hip and knee may be more dangerous than previously thought, according to a special report published in Radiology.
Osteoarthritis of the hip and knee are common and debilitating joint disorders. Physicians often inject anti-inflammatory corticosteroids into the joint to treat the pain and swelling associated with osteoarthritis. The procedure is widely viewed as safe, and patient consent forms mainly mention the risks of hemorrhage and infection among more rare side effects associated with most needle-based procedures.
However, a recent study led by Ali Guermazi, MD, PhD, professor of radiology and medicine at Boston University School of Medicine, found that corticosteroid injections may be associated with complications that potentially accelerate the destruction of the joint and may hasten the need for total hip and knee replacements.
“We’ve been telling patients that even if these injections don’t relieve your pain, they’re not going to hurt you,” Dr. Guermazi said. “But now we suspect that this is not necessarily the case.”
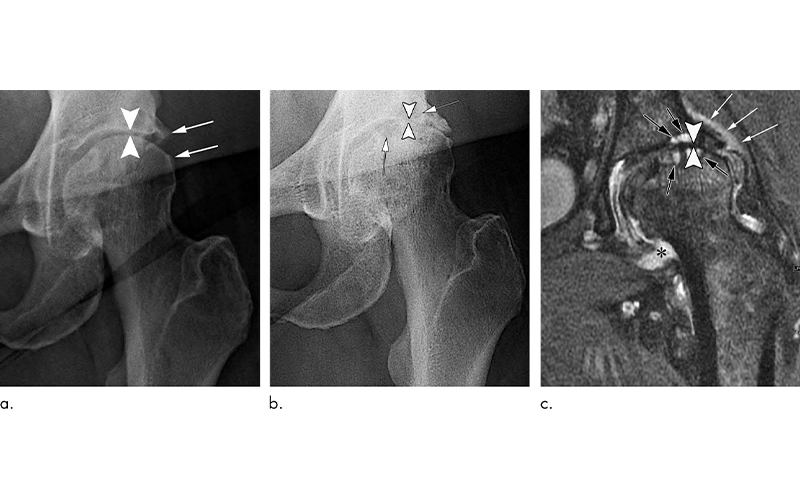
In a review of existing literature on complications after treatment with corticosteroid injections, Dr. Guermazi and colleagues identified four main adverse findings: accelerated osteoarthritis progression with loss of the joint space, subchondral insufficiency fractures (stress fractures that occur beneath the cartilage), complications from osteonecrosis (death of bone tissue), and rapid joint destruction including bone loss.
Review Suggests Caution with Intra-articular Joint Injections
The researchers recommend careful scrutiny of patients with mild or no osteoarthritis on X-rays who are referred for injections to treat joint pain, especially when the pain is disproportionate to the imaging findings. Prior research has shown that these patients are at risk of developing rapid progressive joint space loss or destructive osteoarthritis after injections.
Physicians may also want to reconsider a planned injection when the patient has acute change in pain not explained by X-rays as some underlying condition affecting joint health may be ongoing, the researchers said. Most importantly, younger patients and patients earlier in the course of the disease need to be told of the potential consequences of a corticosteroid injection before they receive it.
“Physicians do not commonly tell patients about the possibility of joint collapse or subchondral insufficiency fractures that may lead to earlier total hip or knee replacement,” Dr. Guermazi said. “This information should be part of the consent when you inject patients with intra-articular corticosteroids.”
With corticosteroid injections so widely used, the potential implications of the study are enormous, according to Dr. Guermazi.
“Intra-articular joint injection of steroids is a very common treatment for osteoarthritis-related pain, but potential aggravation of pre-existing conditions or actual side effects in a subset of patients need to be explored further to better understand the risks associated with it,” Dr. Guermazi said. “What we wanted to do with our paper is to tell physicians and patients to be careful, because these injections are likely not as safe as we thought.”
For More Information
Access the Radiology study, Intra-articular Corticosteroid Injections of the Hip and Knee: Perhaps Not as Safe as We Thought?
Read the accompanying editorial, Risks and Benefits of Intra-articular Corticosteroid Injection for Treatment of Osteoarthritis: What Radiologists and Patients Need to Know.